Overview of Ports
An input port has the direction register bit at 0, meaning the software can only read the values on the input pin.
An output port has the direction register bit at 1, meaning the software can read and write to the pin.
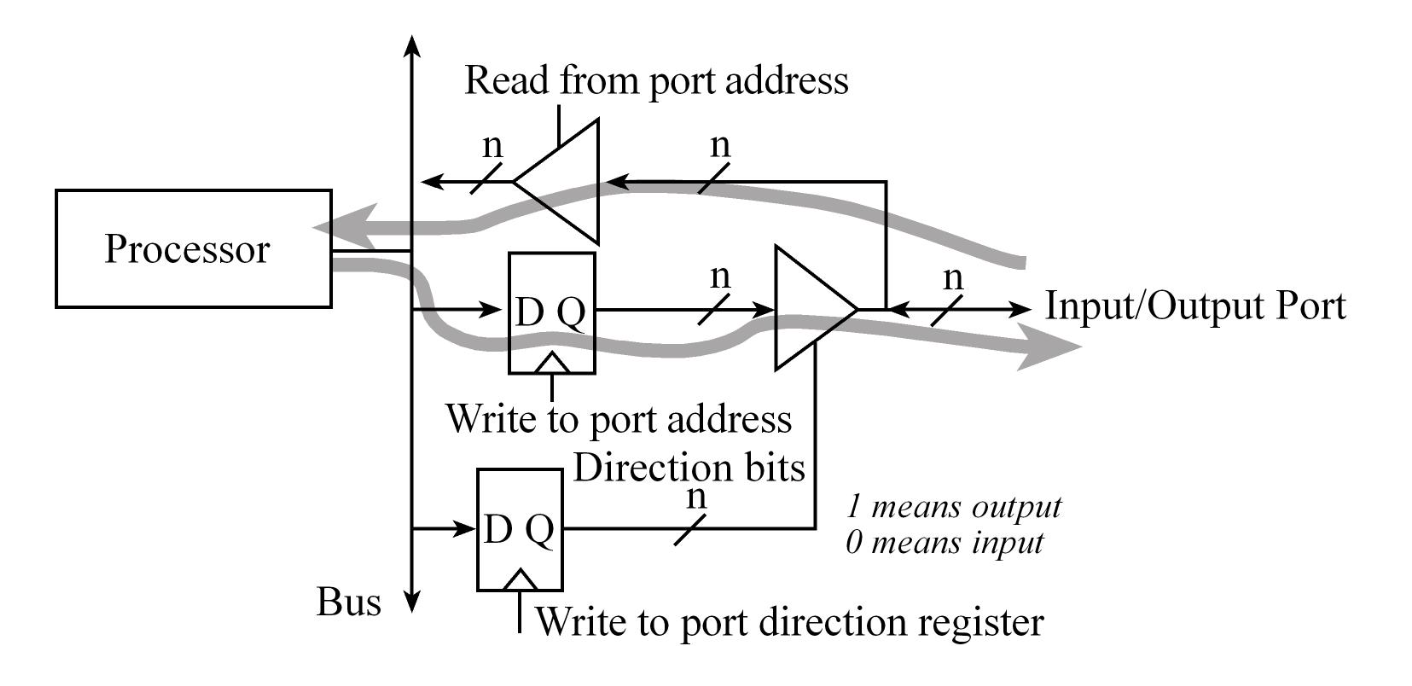
Digital Circuits of an Input and Output Port
The simplest I/O port on a microcontroller is the parallel port.
- A parallel I/O port is a simple mechanism that allows the software to interact with external devices. It is called
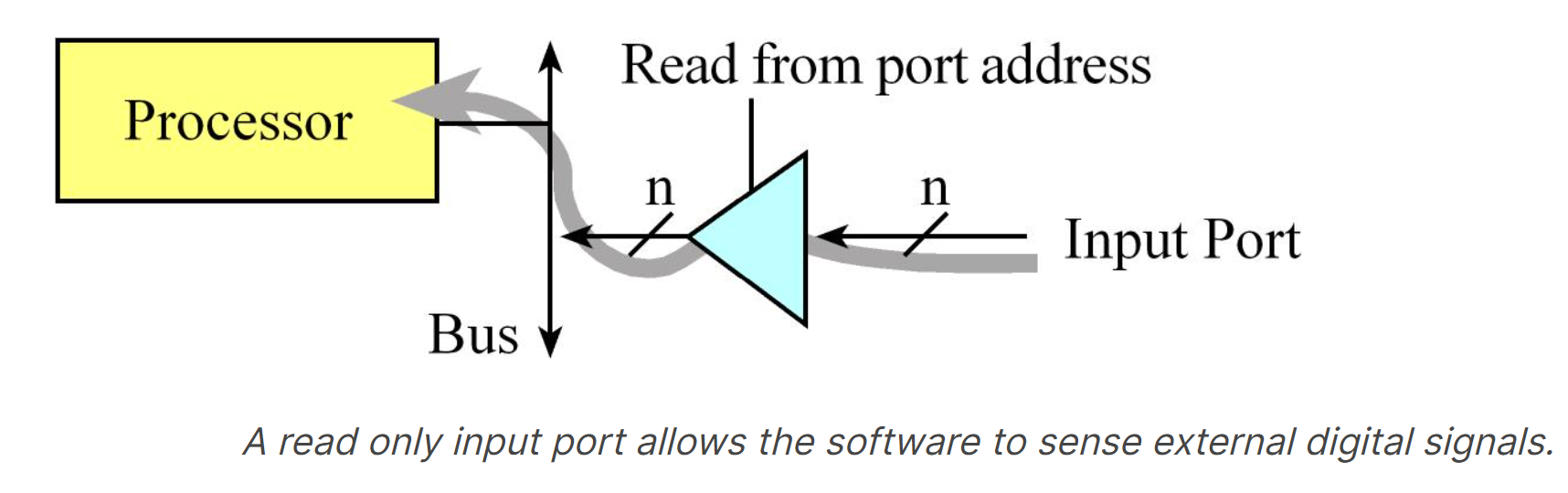
parallelbecause multiple signals can be accessed all at once. - An input port, which allows the software to read external digital signals, is
read only. That means a read cycle access from the port address returns the values existing on the inputs at that time. - In particular, the tristate driver (triangle shaped circuit in Figure below) will drive the input signals onto the data bus during a read cycle from the port address. A write cycle access to an input port usually produces no effect.
- The digital values existing on the input pins are copied into the microcontroller when the software executes a read from the port address.
There are no digital input-only ports on the LM4F/TM4C family of microcontrollers. The LM4F/TM4C family of microcontrollers has 5V-tolerant digital inputs, meaning an input high signal can be any voltage from 2.0 to 5.0 V. On the STMicroelectronics STM32F10xx family, some inputs are 5-V tolerant and others are not.
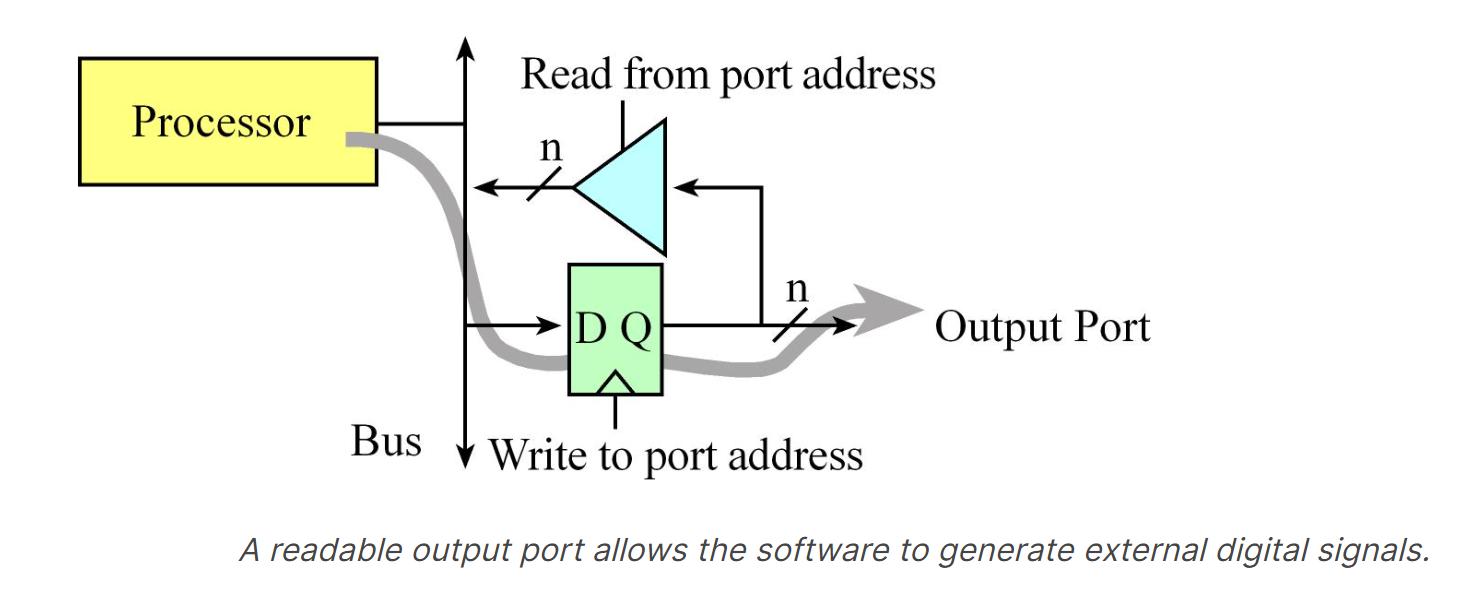
While an input device usually just involves the software reading the port, an output port can participate in both the read and write cycles very much like a regular memory.
Figure below describes a readable output port.
- A write cycle to the port address will affect the values on the output pins.
- In particular, the microcontroller places information on the data bus and that information is clocked into the D flip-flops.
- Since it is a readable output, a read cycle access from the port address returns the current values existing on the port pins.
There are no output-only ports on the LM4F/TM4C family of microcontrollers.
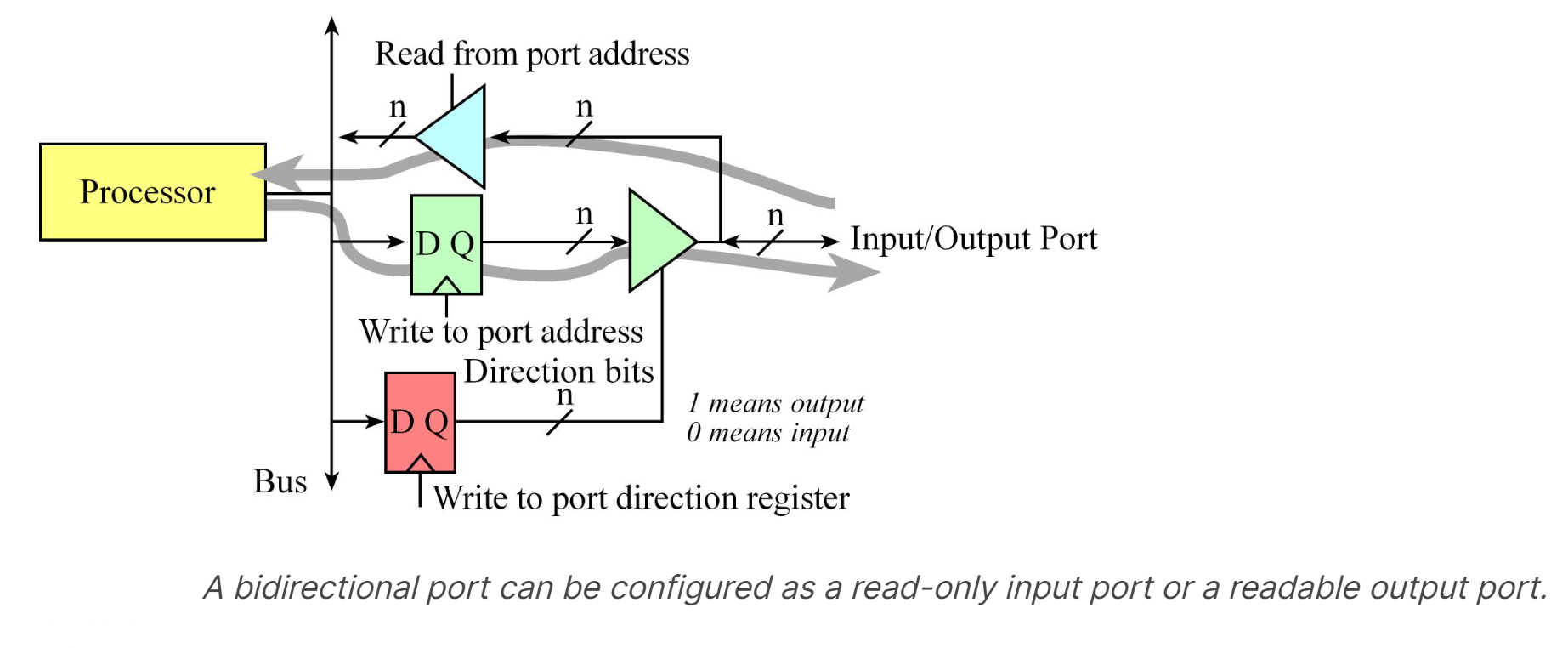
Digital Circuit of a Bidirectional I/O Pin
To make the microcontroller more marketable, most ports can be software-specified to be either inputs or outputs.
- Microcontrollers use the concept of a direction register to determine whether a pin is an input (direction register bit is 0) or an output (direction register bit is 1), as shown in Figure below.
- We define an initialization ritual as a program executed during start up that initializes hardware and software. If the ritual software makes direction bit zero, the port behaves like a simple input, and if it makes the direction bit one, it becomes a readable output port.
Each digital port pin has a direction bit. This means some pins on a port may be inputs while others are outputs. The digital port pins on most microcontrollers are bidirectional, operating similar to Figure below.